Set vs List vs Map in Java
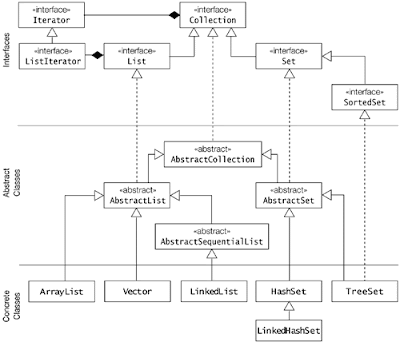
As I said Set, List and Map are interfaces, which defines core contract e.g. a Set contract says that it can not contain duplicates. Based upon our knowledge of List, Set and Map let's compare them on different metrics.
Main difference between List and Set interface in Java is that List allows duplicates while Set doesn't allow duplicates. All implementation of Set honor this contract. Map holds two object per Entry e.g. key and value and It may contain duplicate values but keys are always unique. See here for more difference between List and Set data structure in Java.
Another key difference between List and Set is that List is an ordered collection, List's contract maintains insertion order or element. Set is an unordered collection, you get no guarantee on which order element will be stored. Though some of the Set implementation e.g. LinkedHashSet maintains order. Also SortedSet and SortedMap e.g. TreeSet and TreeMapmaintains a sorting order, imposed by using Comparator or Comparable.
Null elements
List allows null elements and you can have many null objects in a List, because it also allowed duplicates. Set just allow one null element as there is no duplicate permitted while in Map you can have null values and at most one null key. worth noting is that Hashtable doesn't allow null key or values but HashMap allows null values and one null keys. This is also the main difference between these two popular implementation of Map interface, aka HashMap vs Hashtable.
Popular implementation
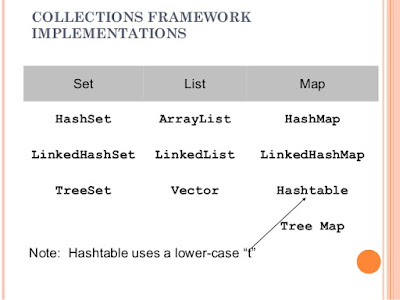
Most popular implementations of List interface in Java are ArrayList, LinkedList and Vector class. ArrayList is more general purpose and provides random access with index, while LinkedList is more suitable for frequently adding and removing elements from List. Vector is synchronized counterpart of ArrayList. On the other hand, most popular implementations of Set interface are HashSet, LinkedHashSet and TreeSet. First one is general purpose Set which is backed by HashMap , see how HashSet works internally in Java for more details. It also doesn't provide any ordering guarantee but LinkedHashSet does provides ordering along with uniqueness offered by Set interface. Third implementation TreeSet is also an implementation of SortedSetinterface, hence it keep elements in a sorted order specified by compare() or compareTo() method. Now the last one, most popular implementation of Map interface are HashMap, LinkedHashMap, Hashtable and TreeMap. First one is the non synchronized general purpose Map implementation while Hashtable is its synchronized counterpart, both doesn' provide any ordering guarantee which comes from LinkedHashMap. Just like TreeSet, TreeMap is also a sorted data structure and keeps keys in sorted order.
Most popular implementations of List interface in Java are ArrayList, LinkedList and Vector class. ArrayList is more general purpose and provides random access with index, while LinkedList is more suitable for frequently adding and removing elements from List. Vector is synchronized counterpart of ArrayList. On the other hand, most popular implementations of Set interface are HashSet, LinkedHashSet and TreeSet. First one is general purpose Set which is backed by HashMap , see how HashSet works internally in Java for more details. It also doesn't provide any ordering guarantee but LinkedHashSet does provides ordering along with uniqueness offered by Set interface. Third implementation TreeSet is also an implementation of SortedSetinterface, hence it keep elements in a sorted order specified by compare() or compareTo() method. Now the last one, most popular implementation of Map interface are HashMap, LinkedHashMap, Hashtable and TreeMap. First one is the non synchronized general purpose Map implementation while Hashtable is its synchronized counterpart, both doesn' provide any ordering guarantee which comes from LinkedHashMap. Just like TreeSet, TreeMap is also a sorted data structure and keeps keys in sorted order.
When to use List, Set and Map in Java
Based upon our understanding of difference between Set, List and Map we can now decide when to use List, Set or Map in Java.
1) If you need to access elements frequently by using index, than List is a way to go. Its implementation e.g. ArrayList provides faster access if you know index.
2) If you want to store elements and want them to maintain an order on which they are inserted into collection then go for List again, as List is an ordered collection and maintain insertion order.
3) If you want to create collection of unique elements and don't want any duplicate than choose any Set implementation e.g. HashSet, LinkedHashSet or TreeSet. All Set implementation follow there general contract e.g. uniqueness but also add addition feature e.g. TreeSet is a SortedSet and elements stored on TreeSet can be sorted by using Comparator or Comparable in Java. LinkedHashSet also maintains insertion order.
4) If you store data in form of key and value than Map is the way to go. You can choose from Hashtable, HashMap, TreeMap based upon your subsequent need. In order to choose between first two see difference between HashSet and HashMap in Java.
That's all on difference between Set, List and Map in Java. All three are most fundamental interface of Java Collection framework and any Java developer should know there distinguish feature and given a situation should be able to pick right Collection class to use. It's also good to remember difference between there implementation e.g. When to use ArrayList and LinkedList , HashMap vs Hashtable or When to use Vector or ArrayList etc. Collection API is huge and it's difficult to know every bits and piece but at same time there is no excuse for not knowing fundamentals like difference between Set, List and Map in Java.


1 comments:
commentsNice article visit good string interview program list
Reply